Diabetic Wound & Skin Care
About Diabetes
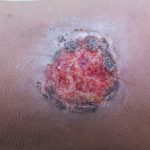 According to the 2022 National Diabetes Facts Sheet, Diabetes currently affects 37.3 million children and adults in the United States. 1.4 million Americans age 18 years or older are newly diagnosed with diabetes each year, one every 23 seconds. In 2018, about 242,000 emergency room visits for adults aged 18 years or older had hypoglycemia as first-listed diagnosis and diabetes as another diagnosis. Statistics show more than 60% of non-traumatic lower-limb amputations performed in the United States were related to diabetes.
According to the 2022 National Diabetes Facts Sheet, Diabetes currently affects 37.3 million children and adults in the United States. 1.4 million Americans age 18 years or older are newly diagnosed with diabetes each year, one every 23 seconds. In 2018, about 242,000 emergency room visits for adults aged 18 years or older had hypoglycemia as first-listed diagnosis and diabetes as another diagnosis. Statistics show more than 60% of non-traumatic lower-limb amputations performed in the United States were related to diabetes.
What is Diabetes?
It is estimated that about 11.3% of the US population (about 37.3 million people) have diabetes; that’s 1 in 10 Americans. Studies show 8.5 million Americans have undiagnosed diabetes. In the United States, approximately 5-10% of the population with diagnosed diabetes have type 1 diabetes; approximately 90-95% has type 2 diabetes. Other, rare types of diabetes also exist at a rate that is difficult to accurately estimate.
Managing Your Diabetes
Your body needs energy to perform daily activities. This energy comes from foods containing protein, fats, and carbohydrates that are broken down by the body and changed into glucose (blood sugars). Insulin is a hormone that is needed by the body to utilize glucose. Diabetes occurs when the body cannot make use of the glucose in the blood, either because the pancreas isn’t producing enough insulin (Type 1) or the insulin produced is not used effectively, resulting in high blood sugar (Type 2).
The goal of treatment for all types of diabetes is to keep the glucose within a normal range. Diabetes can often be controlled with diet and exercise alone, although some people may need oral medications or insulin injections. Research has shown that keeping glucose levels close to normal may help prevent or delay complications such as eye, heart, kidney and nerve damage. Balancing diet, exercise and medication is the key to good control. Daily monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. Use the results from your glucose monitor as a tool to gauge how your body is doing throughout the day. By managing your life and illness today, you will reduce the complications of diabetes tomorrow.
Early Detection
- Inspect your feet daily.
- If you detect any break in the skin, contact your doctor immediately to schedule an appointment.
- Cleanse your wound with AMERIGEL Saline Wound Wash. Apply AMERIGEL Hydrogel Wound Dressing directly to the wound. Cover the wound with a sterile gauze pad or band aid.
- Follow-up with your doctor.
Prevention
- Inspect your feet daily.
- Wash and dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Apply AMERIGEL Care Lotion to your feet daily to hydrate your skin.
- Keep your toenails trimmed short and straight across.
- Wear comfortable shoes and clean socks that properly fit your feet.
- Avoid wearing the same shoes two days in a row.
See your podiatrist for an annual foot check-up and any severe or persistent problems.

