Cuts & Abrasions
What are Cuts and Abrasions?
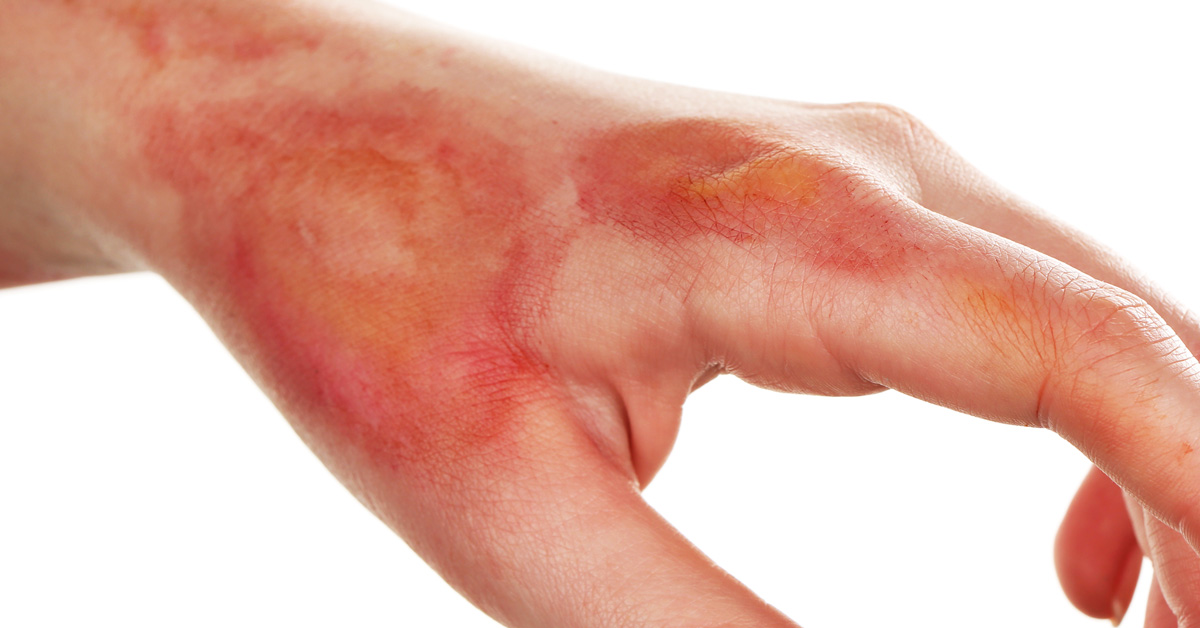
Cuts and abrasions are common injuries that occur in everyday life. They can range from mild to severe in degree of severity. Abrasions can be painful because they expose many nerve endings in the skin. They rarely cause major bleeding, however, and can be treated at home.
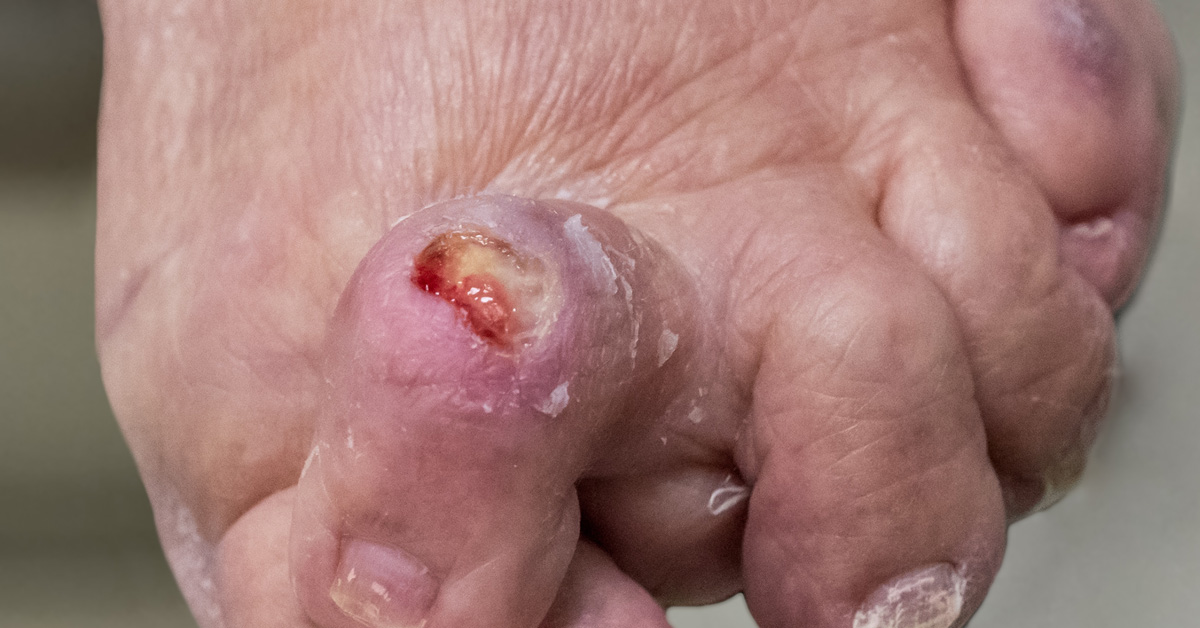
Cuts and abrasion wounds must be properly treated to avoid infection and promote rapid healing. The injury may heal at a different rate depending on factors such as a person’s overall health, age, and diet. People with weakened immune systems, diabetes, medications that cause skin dryness and fragility, and the elderly with thinner skin are considered at greater risk.
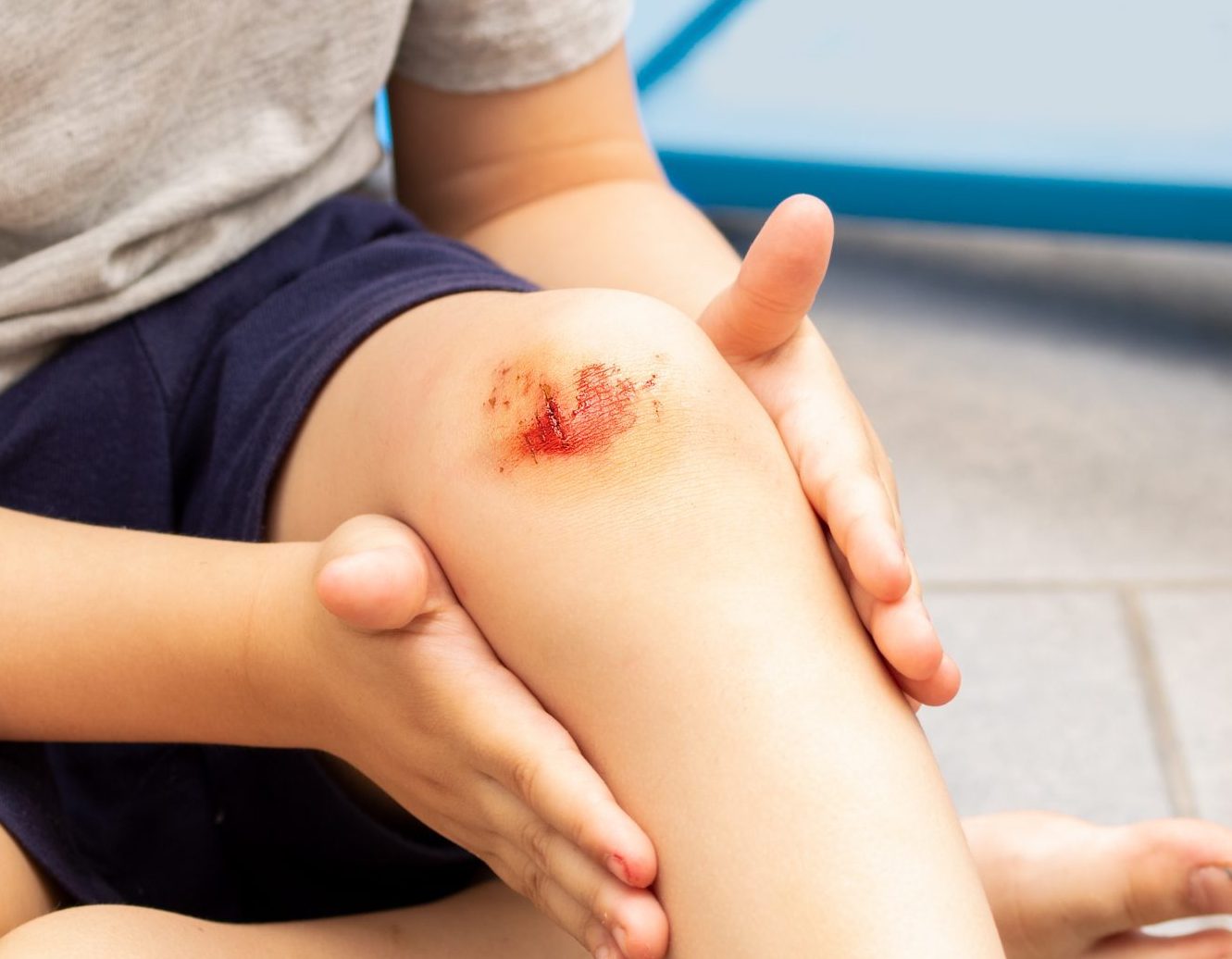
What is the Difference Between a Cut and an Abrasion?
Cuts and abrasions are classified as minor or major wounds. While most of these wounds can be successfully treated at home, it is important to clean, treat, and protect the wound properly.
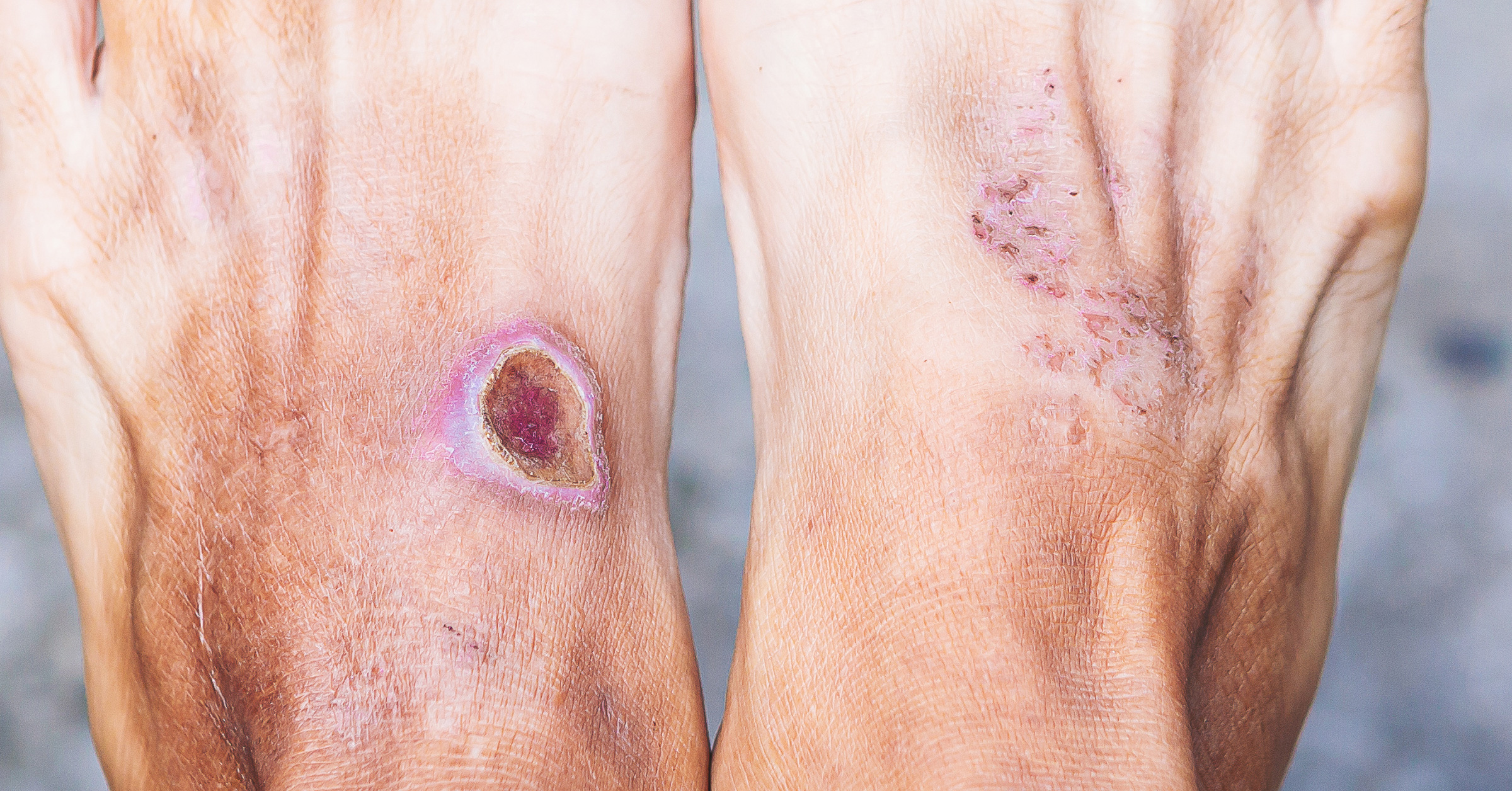
- Cuts – A cut can be caused by various objects that may be blunt or sharp. Depending on the injury, underlying blood vessels can be punctured. Ensure that your tetanus vaccination is up to date if you have puncture wounds, such as those from a nail.
- Abrasions – A skin abrasion is a small wound that develops from skin rubbing or experiencing friction against a rough surface. Other terms that may be used are scrape, graze, and road rash.
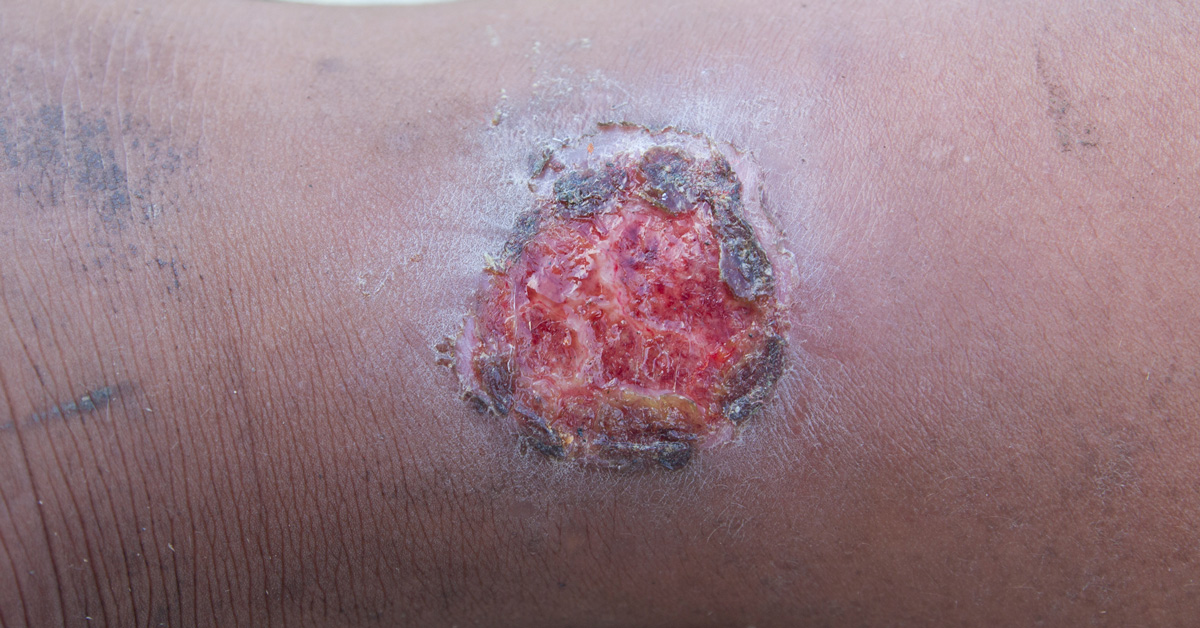
Minor cuts and abrasions typically form a scab within a few days to protect the wound from dirt and germs as new skin grows. If a cut wound is deep and gaping, stitches may be required to promote healing, reduce scarring, and prevent infection. Deep wounds should be stitched as soon as possible.
How To Treat Cuts and Abrasions at Home
- STOP the bleeding with a clean cloth or gauze dressing and hold pressure. If the bleeding doesn’t stop within 10 minutes, keep applying pressure and seek help from a doctor.
- WASH your hands with soap and water. You may have bacteria or other substances on your hand that could cause infection.
- CLEANSE the cut or abrasion with cool water or AMERIGEL® Saline Wound Wash to remove the dirt and debris. Do not scrub the wound vigorously, as this could cause additional damage and bleeding. Remove debris. If there are visible fragments of grass, rocks, or dirt, you should remove them with caution.
- APPLY a thin layer of AMERIGEL Hydrogel Wound Dressing to the wound and cover with a clean non-stick dressing. This advanced hydrogel technology helps open wounds heal faster by giving them the constant moisture they need to heal. Then, cover the wound with a bandage, such as AMERX® Bordered Gauze.
- CHANGE DRESSING daily. Be sure to cleanse the wound with water or normal saline. Reapply AMERIGEL Hydrogel Wound Dressing and repeat steps until the wound is healed.
- CHECK for infection as the wound heals. If you are experiencing increased pain, swelling, warmth, redness, or pus; call your doctor.
NOTE: If you are experiencing any symptoms suggestive of a medical emergency, always contact a physician or seek urgent care immediately.